P-ISSN: 2349-6800, E-ISSN: 2320-7078
Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies
2016, Vol. 4, Issue 3
Prospects of using carbohydrates as supplemented-diets and protein rich mixture as alternative-diet to improve the quality of venom produced by Apis cerana L.
Mohammed Abusabbah, Wei Hong Lau, Mohammed EE Mahmoud, Ashraf M Salih, Dzolkhifli Omar
In this study, an attemptrnto assess the effect ofrncarbohydrate supplants and protein rich mixture was studied. Honeybees were fedrnon glucose, fructose and maltose for two monthsrnto guarantee feeding of the new generation on the new introduced diet, besides,rnbees were artificially fed on sugar (sucrose in water 1:1) and protein richrnmixture consisting of soybean flour, dried yeast and dry skim milk, withrndifferent portions. Control group of bees was naturally fed of pollens grain,rnfor comparison purposes. Thernresults showed that among the supplemented-carbohydrate diets to the beehives,rnmaltose sugar was found to be the best quality of bee venom, which gave thernhighest concentration of melittin, phospholipase A2 and apamin ofrn535.21±17.73, 374.49±18.94 and 130.36±12.05 µg/µl respectively. The comparisonrnof the alternative diets revealed that the protein rich mixture is better thanrnsucrose diet. While, no significant difference in comparison with the naturalrnpollen grains diet for yielding venom with high quality, and the venom majorrncomponent concentrations were 585.67±12.89, 439.48±63.64 and 120.61±9.01 µg/µlrnfor melittin, phospholipase A2 and apamin, respectively.
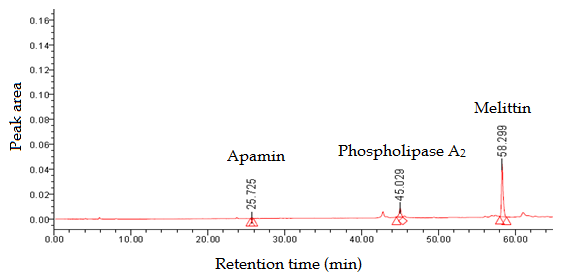
Fig. 1: HPLC Chromatogram of the Standard of the Honeybee Venom Major Components
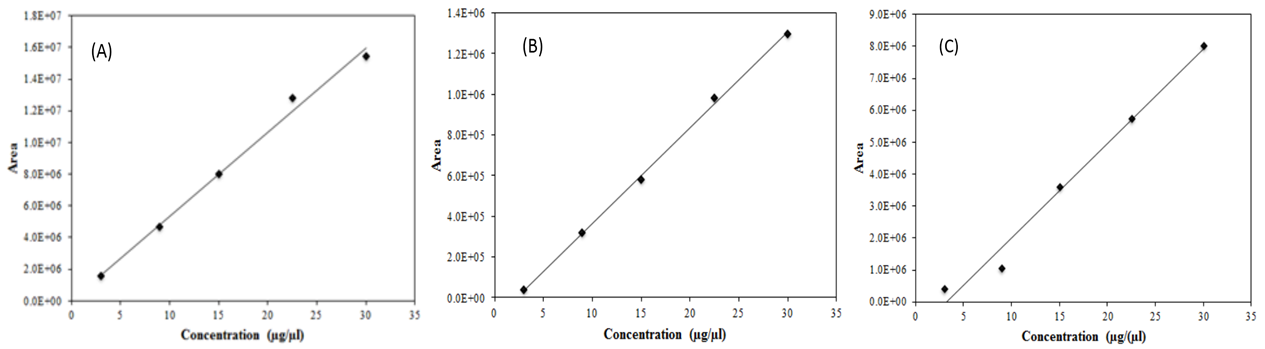
Fig. 2: The standard linear line of (A): Melittin, (B) Apamin; and (C) Phospholipase A2
Pages : 23-26 | 2465 Views | 167 Downloads
How to cite this article:
Mohammed Abusabbah, Wei Hong Lau, Mohammed EE Mahmoud, Ashraf M Salih, Dzolkhifli Omar. Prospects of using carbohydrates as supplemented-diets and protein rich mixture as alternative-diet to improve the quality of venom produced by Apis cerana L.. J Entomol Zool Stud 2016;4(3):23-26.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links
Important Links










