P-ISSN: 2349-6800, E-ISSN: 2320-7078
Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies
2019, Vol. 7, Issue 6
Effect of insect feeding on biochemical changes in rice plant
A Nayak, MJ Baig, PK Mohapatra and KS Behera
Rice crop is attacked by several insect pests from nursery to harvest. Investigation was carried out to determine the effect of feeding damages caused by the insect pests yellow stem borer (YSB), white backed plant hopper (WBPH), brown plant hopper (BPH) and leaf folder (LF) on the biochemical parameters of rice plant. Rice plants damaged by these insects were analyzed for the quantitative and qualitative changes in biochemical profile e.g. starch, nitrogen, soluble sugar, protein, total chlorophylls and carotenoids. The experiments have been conducted in a rice cultivar TN1 susceptible to all the insects. Standard biochemical procedures were followed to analyse different biochemical parameters. The concentration of starch in leaf was highest in the control, followed by YSB, WBPH, BPH and LF damaged plants in a sequence. Feeding by WBPH and BPH reduced the total nitrogen concentration of the leaf more compared to the other two insects. Total soluble sugar concentration in leaves of damaged plant was the maximum in the control plants exceeding the level of 20 (mg/g fresh weight) and insect feeding reduced it by more than half. YSB and BPH effects were more severe in comparison to the other two insects. Similar to the carbohydrates, leaf protein concentration (mg/g fresh weight) was also declined by insect feeding. In sharp contrast to the biochemicals, insect feeding did not have significant effect of chlorophyll a concentration of the leaf. Similar to chlorophyll a, the concentration of chlorophyll b was not influenced by insect feeding severely and the effects were marginal. The concentration of leaf carotenoids did not change much with insect feeding, but reduced marginally compared to the control plants. The level of reduction was maximum for BPH infestation.
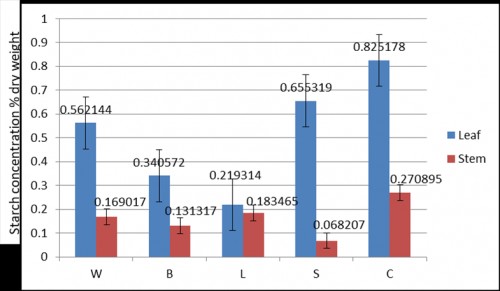
Fig. 1: Effects of insect damage on starch concentration (% of dry weight) of leaf and stem tissues of sensitive rice cultivar TN 1 during the vegetative stage
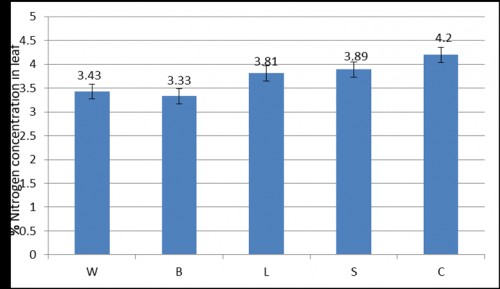
Fig. 2: Effect of insect damage on nitrogen concentration (% of dry weight), of leaf of sensitive rice cultivar TN 1 during the vegetative stage.
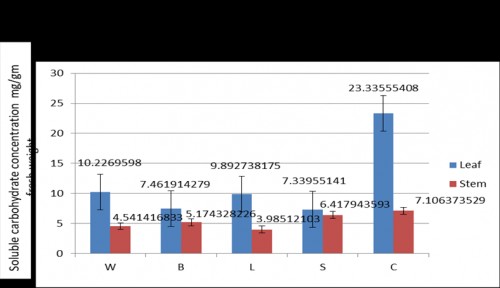
Fig. 3: Effect of insect damage on soluble carbohydrate concentration (mg/g fresh weight), of leaf and stem of sensitive rice cultivar TN 1 during the vegetative stage of development.
Pages : 138-142 | 886 Views | 220 Downloads
How to cite this article:
A Nayak, MJ Baig, PK Mohapatra, KS Behera. Effect of insect feeding on biochemical changes in rice plant. J Entomol Zool Stud 2019;7(6):138-142.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links
Important Links










