P-ISSN: 2349-6800, E-ISSN: 2320-7078
Journal of Entomology and Zoology Studies
2019, Vol. 7, Issue 6
Prevalence of wound infection in wild and captive elephants (Elephas maximus) of Assam
A Buragohain, G Mahato, BC Das, A Phukan, KK Sarma and NN Barman
A total number of 163 elephants were examined during one year (March, 2017 to April, 2018) consisting 24 wild and 139 captive elephants. The prevalence of wound infection in wild and captive elephants was 25. 00% and 28. 78% respectively, with an overall prevalence of 26. 89%. However, the highest prevalence (46. 15%) was recorded in private elephants. Age wise prevalence was highest in 31- 40 yearsof age group (42. 85%). The prevalence of wound infection was highest in female of private captive elephant (50. 00%) followed by departmental captive elephant (25. 00%). In wild elephant the wound infection was higher in male elephant (31. 25%) than female (12. 50%). The prevalence of wound infection in captive elephant was higher during winter season (39. 28%) and lower in rainy season (7. 50%). The higher prevalence was recorded in summer season (66. 66%) in wild elephant but no wound infection in autumn season.
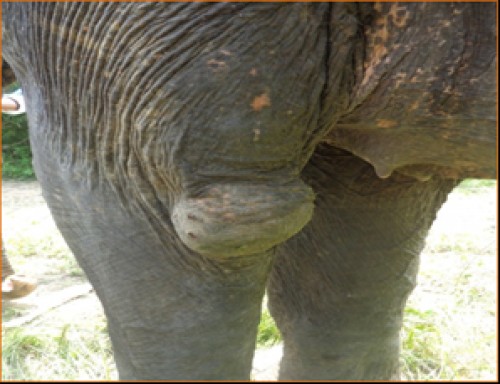
Fig. 1: Wound in Elbow
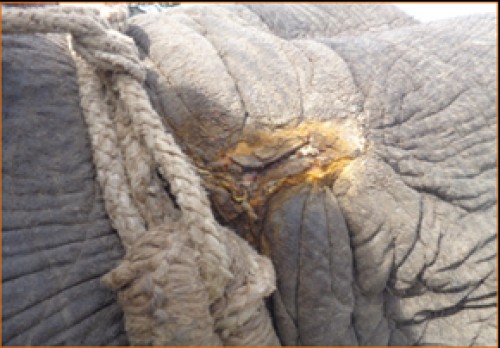
Fig. 2: Wound in Neck
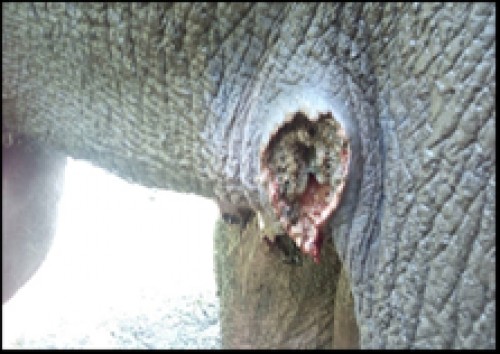
Fig. 3: Wound in stifle region
Pages : 171-174 | 823 Views | 149 Downloads
How to cite this article:
A Buragohain, G Mahato, BC Das, A Phukan, KK Sarma, NN Barman. Prevalence of wound infection in wild and captive elephants (Elephas maximus) of Assam. J Entomol Zool Stud 2019;7(6):171-174.
Related Journal Subscription
Important Publications Links
Important Links










